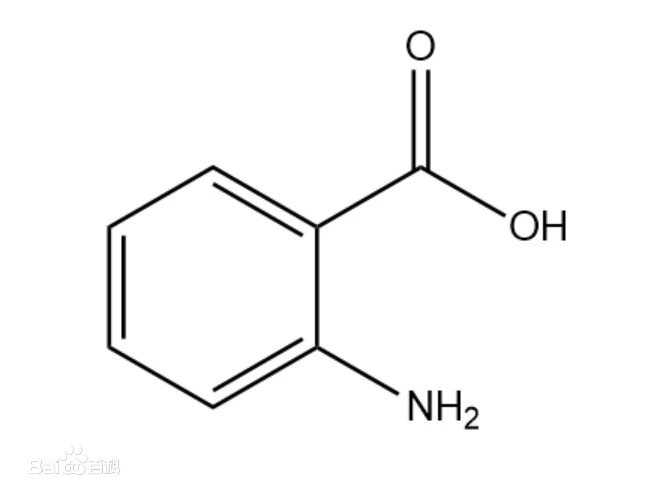
Anthranilic acid

Name |
Anthranilic acid | Boiling point | 311.9 ℃ |
Water soluble | 5.7g/L (25 ℃) | ||
Alias | 2-Aminobenzoic acid | Density | 1.412 g/cm³ |
Chemical formula | C7H7NO2 | Exterior | White to pale yellow crystalline powder |
Structural formula |
| Flash point | 150 ℃ |
Molecular weight | 137.136 | Application | Used as an intermediate for dyes, medicines and fragrances |
CAS login number | 118-92-3 | Security Description | S26;S36;S39 |
EINECS login number | 204-287-5 | Hazard Symbols | Xi |
Melting point | 144-148 ℃ | Hazard description | R36/37 |

Density | 1.412g/cm3 |
Melting point | 144-148℃ |
Boiling point | 311.9℃ |
Flash point | 150℃ |
Exterior | White to pale yellow crystalline powder |
Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, ether, hot chloroform, hot water, slightly soluble in benzene, insoluble in cold water |

Toxicological data:
Acute toxicity: mouse oral LD50: 1400mg/kg.
Ecological data:
The substance is harmful to the environment and can cause pollution to water and the atmosphere. Organic acids are easy to form acid rain in atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physical changes. Therefore, when the pH value drops below 5, it will cause serious harm to animals and plants, and the reproduction and development of fish will be seriously affected. Water acidification will also lead to changes in the composition and structure of aquatic organisms. Acid-tolerant algae and fungi increase, while root plants, bacteria and vertebrates decrease, and the decomposition rate of organic matter decreases. Acidification can seriously reduce or die of fish in lakes and rivers.

Safety term
S26: After accidental contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
S36: Wear appropriate protective clothing.
S39: Wear goggles or a mask.
Risk term
R36/37: Irritating to eyes and respiratory system.

Used as intermediates in medicine, dyes, spices and pesticides. In terms of dyes, it can be used to prepare anthraquinone dyes, azo dyes and indigo dyes; it is also used as a chemical reagent for the determination of silver, magnesium, mercury, cadmium, nickel, zinc, cobalt, lead, cerium, copper, manganese, palladium and It is a complexing reagent for various metals such as uranium; it can also be used in organic synthesis to produce compounds such as 3-hydroxyindole and methyl anthranilate.